work carried out
2023 - jan - 23
in DQN network as for the sequential layers
inputs -> 16 activation relu linear 16 -> 16 activation relu output 16 -> num actions
observation
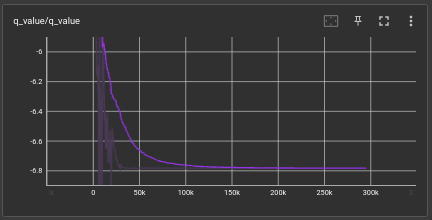
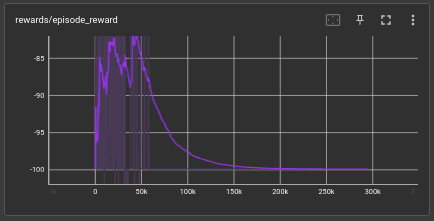
the q value mean was a constant and in a stable position
conclusion
as for the control state i've removed the exploration by removing the epsilon
because of this in order to be stabilize the model it chooses to do nothing at all and this is a good example where exploration was removed and network is not enough to determine a stable position.
this experiment was a failed
next is to introduce the epsilon and see how it performs
2023 - jan - 24
tasks to do
- [x] add a player where it generates random values with no probability to indicate a autistic behavior
- [x] when feeding players into the environment introduce them one by one
- for example introduce medium player first and run the environment for 10000 steps and then add another player where it has similar features like the player introduced at the beginning and now the environment has 2 players and again run it for like 10000 steps and so on introduce other players as well to the environment.
- [ ] add more state sets to the world where the model can freely move more on the environment.
problems accord during the process
adding all the problems accord during the process
players were added when there is a reset on the environment. and a player was added every 100000 steps.
interesting things saw during the process
player feeding was done in 2 different ways,
- average type of 3 players in the beginning and then the 3 types of best players and last the low type players
- best 3 players first and then the average and finally the low players
observation 1
when feeding average players first
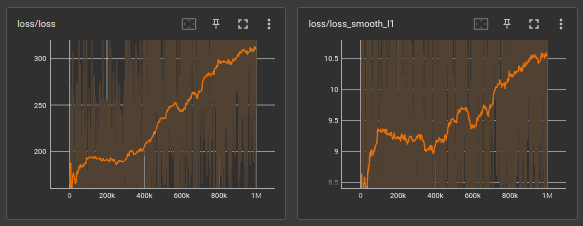


when feeding best players first


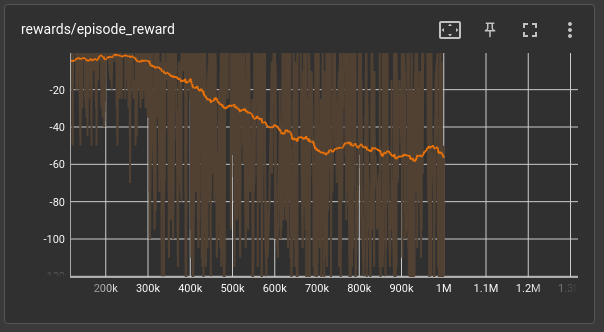
Note
As for the observation we can see that after adding the 3rd player no matter what it generally starts to go down on accuracy.
-
maybe it's because of the learning rate was decayed and a sudden change can't be handled by the model, so changing that back again to a higher value and gradually decaying back will help the model to gain it in a positive manner.
-
another suggestion is to add more dense layers to the model which it can learn more.
- but need to identify a proper method of adding new layers without trying randomness.
2023 Jan 25
as for the reward not being achieved, there can be few reasons and these are the things thant should be focused in order to maintain a result
reward not being achieved
If the reward in a reinforcement learning (RL) problem is not being achieved and is instead stabilizing at a negative value, it could be an indication of a poor or suboptimal policy being learned by the RL agent. There are several potential reasons for this:
-
Poor exploration: The agent may not be exploring the state space effectively and getting stuck in a suboptimal region. In this case, increasing the exploration rate or using more advanced exploration methods such as count-based exploration or intrinsic motivation may help.
-
Inadequate function approximation: If the agent is using a function approximator (such as a neural network) to represent the policy, it may not have enough capacity or be sufficiently expressive to capture the optimal policy. Increasing the complexity of the function approximator or using more data to train it may help.
-
Inadequate reward signal: The reward signal may not be providing enough information for the agent to learn the optimal policy. In this case, carefully designing the reward function or shaping the rewards to guide the agent towards the optimal policy may be helpful.
-
Stochasticity in the environment If the environment is stochastic, the agent may be unable to learn from the rewards and get stuck in poor regions. Try to reduce the stochasticity by adding more deterministic elements to the environment.
-
Poor learning algorithm The agent may be using a poor learning algorithm or the hyperparameters of the algorithm may not be well-tuned. In this case, experimenting with different learning algorithms or fine-tuning the hyperparameters may help.
It is essential to understand the problem and the environment, as well as experimenting with different approaches and techniques to find the one that works best for the specific problem at hand.